
What is the Strategic Planning Framework “6e”?ストラテジックプランニングフレームワーク「6e」とは?
Nearly 70% of corporate performance declines are attributed to marketing issues such as poor sales, making marketing strategy the highest priority in business strategy. However, traditional marketing strategies often lean heavily toward sales promotion, advertising, and PR, frequently overlooking the need for alignment with organizational structure and operational processes. As a result, many companies fail to achieve effective marketing outcomes.
From this perspective, we developed the foundational framework ‘6e’ to solve corporate challenges.
“6e” represents the essential elements (elements) of corporate activities. Based on practical holistic marketing, “6e” blends various management strategy tools. It classifies and positions corporate activity elements into six categories: “1. Research & Analysis,” “2. Management Strategy,” “3. Business Strategy,” “4. Marketing,” “5. Management,” and “6. Operations.” It is a strategic planning framework designed for continuous transformation, constantly updated through feedback from practice and ongoing research.
The Six Processes of “6e”
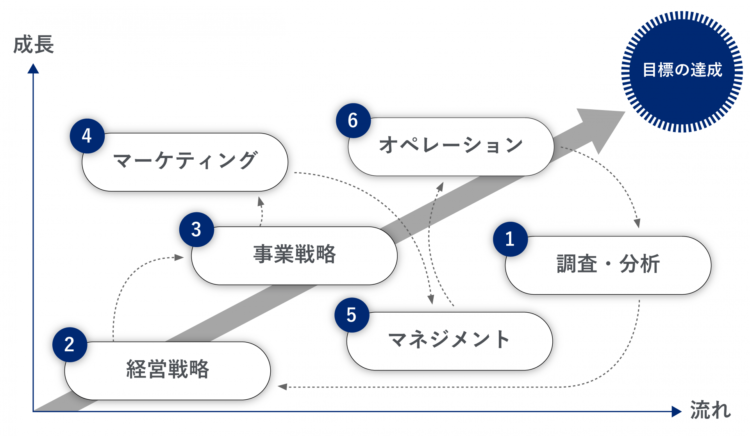
For any challenges facing a company’s products or services, we first gather information through interviews with the responsible personnel, top management, and sometimes directly with the president. Based on this preliminary research and incorporating environmental analysis (external and internal environments, etc.), we formulate management strategy (1), develop business strategy (2), plan marketing activities (4), and in management activities supporting marketing, we redesign organizational structures prone to becoming bottlenecks, review and optimize personnel, training, and finance (5).
Finally, we concretize operations for each measure and task, verify and improve the execution results of each strategy (6), thereby achieving comprehensive strategic execution support for corporate management. Thus, “6e” is a powerful framework that views a company’s marketing activities as integral to the company itself. By continuously refining the marketing environment, it provides robust support for reliable problem resolution.
Features of the “6e”
| Feature 1 | Based on holistic marketing principles, we adopt a unique approach that views the company as a whole and designs strategic activities tailored to each company's specific needs. |
|---|---|
| Feature 2 | This is an evolutionary framework centered on continuous updating. Strategists monitor the company's environment and consumer trends, incorporating the latest strategic planning methods to adapt flexibly. |
| Feature 3 | We pursue low-cost, high-quality solutions for strategy design, products, and tools, aiming to maximize effectiveness while minimizing costs. |
Components of “6e”「6e」の構成要素
1Survey Analysis
Based on the 『6e』 framework, research and analysis are crucial for identifying challenges faced by companies and their services/products, formulating hypotheses, validating them, and designing optimal strategies. By analyzing findings, we review current strategies and derive guidelines for strategic planning.
1 Preliminary Research
Establishing shared understanding with the client company (organization) and gaining an accurate, bird’s-eye view of the current situation enhances the precision of research and analysis. This, in turn, improves the accuracy of subsequent strategy and tactic design. Conducting preliminary research before implementing research and analysis is recommended.
★Preliminary Interviews: Conduct interviews with the president and product/business managers to gather information about challenges.
★Corporate Diagnostic Navigator: Have the president and management undergo a diagnostic assessment to grasp the company’s overall current capabilities.
2 External Environment Analysis
External Environment Analysis involves extracting and analyzing elements of “Opportunity” and ‘Threat’ from the “external” environment surrounding the company, using a multifaceted perspective.
★External Environment (Macro) Analysis: Analyzes environmental factors that are difficult for the company to control and do not directly involve company or business operations, such as the political, economic, social, and technological environment.
★External Environment (Micro) Analysis: Analyzes environmental factors directly involved in company/business operations, such as market size, customer trends, and competitor movements.
3 Internal Environment Analysis
Internal environment analysis evaluates the company’s internal strengths and weaknesses in relation to the success factors of the market.
4 Positioning Analysis
Based on the findings from the external and internal environment analyses, this step analyzes the company’s position within the market. The objectives are to understand the differences from competitors, determine whether the competitive position is highly contested, and identify any advantageous positions where competitors are absent.
5 Target Analysis
Based on the findings from the external and internal environment analyses, this step analyzes the target. If target information not fully captured by the external/internal environment survey exists, additional research is conducted.
6. Integrated Analysis
Integrated analysis involves extracting “opportunities” and “threats” from the external environment analysis, and ‘strengths’ and “weaknesses” from the internal environment analysis. After analyzing positioning and targets, these elements are combined to derive the core of strategic option planning.
7 Brand Lift Survey
Quantitatively evaluates the effects and impact of advertisements and campaigns on consumers, measuring indicators such as brand awareness, favorability, perception, and purchase intent.
2Philosophy and Business Domain
Strategic design and management are crucial for ensuring the reliable implementation of business strategies. However, strategic design and management require guiding principles such as “What does the company aim to achieve?”, “What kind of company should it be from society’s perspective?”, and “What actions should the company take?” This connects to the formulation of business strategies and strategic planning that addresses every phase of corporate operations.
1 Confirming and Redefining the Philosophy
The philosophy is a crucial concept for clarifying an organization’s direction and goals. Before designing specific strategies, we confirm why the company exists.
2 Portfolio and Domain Reorganization
When operating multiple businesses, it becomes necessary to discern which ventures warrant resource allocation and which should be exited. Considering each current business’s profitability, stability, and growth potential, the company must evaluate how its portfolio should be structured moving forward. Furthermore, the corporate domain and business domain—the explicit areas, fields, and scope of operations for the entire company—must also be defined.
3 CI Review and Redefinition
CI involves systematically organizing a company’s core values based on its founding principles, business activities, and corporate social responsibility (CSR), then sharing these redefined principles and action guidelines internally and externally to enhance corporate activities. It forms the “core of the company” and profoundly influences the ‘people’ and “products/services” that generate profits. Properly defining CI enables the extraction of strengths from the company and its products/services.
4 CI Penetration
Corporate brand represents the essence of the company itself. It is an intangible asset that shapes the image held by customers, employees, shareholders, and others. Companies must manage the brand that expresses their uniqueness and build their own corporate brand.
Branding is a vital method for selling products and services at higher prices and in greater quantities without getting caught up in price competition, thereby increasing corporate profits and ensuring long-term business stability. It is essential to correctly value (i.e., brand) the company without allowing CI to diverge significantly from reality.
3Business Strategy
Corporate strategy and company-wide strategy concern the entire enterprise or corporate group, designing the selection and abandonment of businesses and resource allocation among multiple businesses. In contrast, business strategy (or competitive strategy) designs how to build and maintain competitive advantage at the level of individual business units.
1 Confirming and Redefining BI
BI (Business Identity) clearly articulates the concept a business brand wishes to project—what it aims to symbolize. Based on research and analysis, it involves redefining products/services to address all challenges they face. Redefining BI entails revisiting the product concept, communication messages, target audience, and other aspects of “who the product/service is for,” and reworking “how the product/service will be delivered.” Constant review leads to business strengthening and development.
2 Formulating Business Strategy (Selecting Strategic Methods and Means)
Based on the defined BI and research findings, we formulate the fundamental business strategy for how to compete in the market and against competitors.
2-1 Competitive Strategy
We examine how to compete in the market and against competitors, including positioning.
2-2 Strategy for Methods and Means
We formulate strategic plans to achieve objectives. Broadly, these include: ① International Strategy, ② M&A/Alliances, and ③ Development.
3 Action Design
3-1 Activity System
We establish activity systems as mechanisms to further strengthen our competitive advantages. Activity systems are deeply intertwined with the quality of services provided to customers, making them a critical element in building growth strategies.
3-2 Business Model
We design the overall structure (business model) for how value is created, delivered, and monetized. The business model explicitly defines the revenue-generating mechanism, making it a crucial component in constructing growth strategies.
3-3 Growth Strategy
Even after determining competitive positioning and specific methods within the business strategy, operations may not immediately proceed as envisioned. Testing in the market and setting intermediate goals to achieve the ultimate objective are necessary to establish the company’s ideal position and shape the market.
4 BI Implementation
Branding is a vital method for avoiding price competition, selling products and services at higher prices and in greater volumes, increasing corporate profits, and ensuring long-term business stability.
4Marketing
Product strategy, price strategy, and promotion strategies such as PR, WEB, Event, Mass Media, OOH, campaign, and distribution strategy, and planning from the strategy planning that has been derived sales strategy, all of the marketing activities, to implement the proposal in line with the creative.
1. Product Strategy
The strategy involved in the product. Product strategies can be divided into “strategic planning for product items,” “decision making,” “strategic planning for product lines,” and “decision making.” In addition, among the “core functions”, “forms” and “ancillary functions” that make up the product items, one of the elements that the marketer observes is “form”.
The form of the product has five characteristics: features, style, brand name (naming), package, and quality. The key to thinking about a product strategy is knowing its product characteristics. The product strategy will change depending on who buys the product, what characteristics it has, how many types it has, and what price range it has.
2. Pricing Strategy
The price strategy is based on profit planning, and there are three main categories: “high price strategy,” “medium price strategy,” and “low price strategy.” In addition, it is necessary to consider flexibly in selling products, such as discounts on promotions, such as infomercials, and it can be said that it is an important factor for planning a marketing strategy as well as a company.
3. Promotional Strategy
The customer’s consumption behavior is closely influenced by the promotion strategy, and it is developed by incorporating various factors such as commodity and price.
Therefore, it is important to know how customers and consumers perceive companies, goods, and services and make purchasing and introduction decisions based on the consumption behavior model.
It is thought that the movement of the promotion strategy can be more understood by knowing how people move.
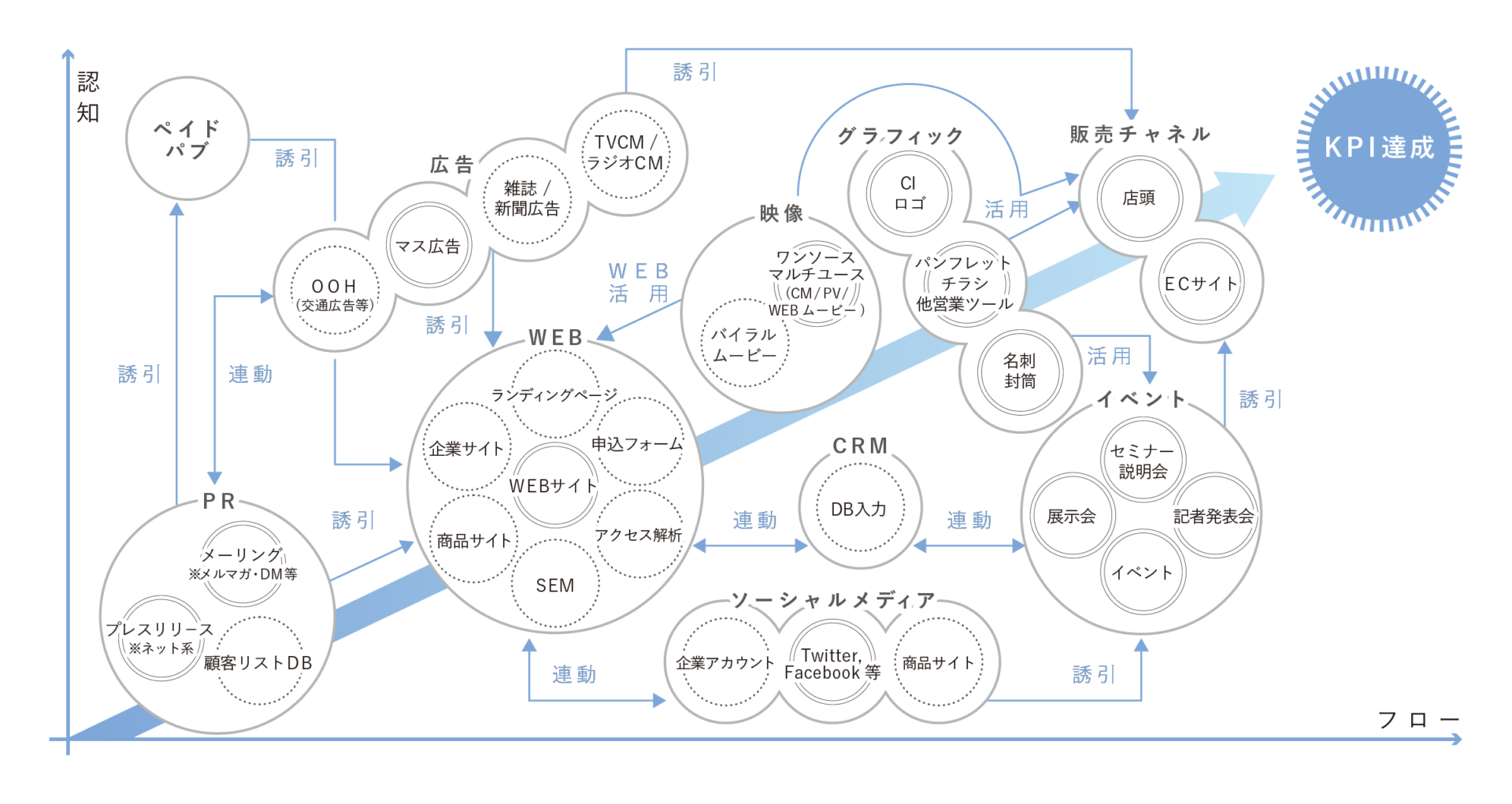
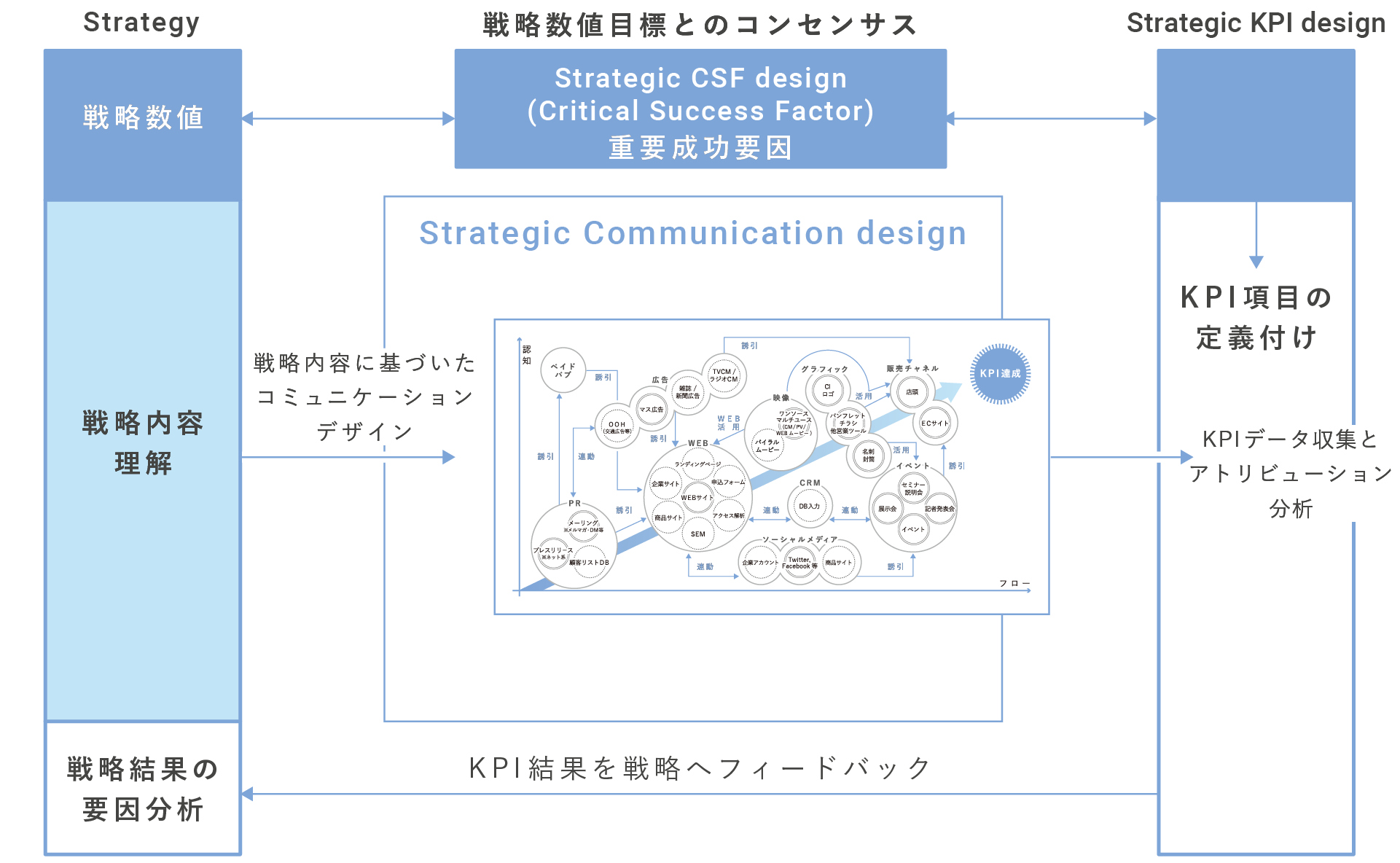
■Strategic Communication Design
As for our promotional strategy, we consider that organic cooperation is important as well as strategic, and we are implementing various advertising products based on the following communication map.
The communication map is a schematic diagram of an idea that recognizes the vertical axis and positions the horizontal axis in the implementation flow and can view the organic implementation towards the goal, including advertising production from PR.
4 Place
Place strategy is a crucial strategy for product sales. Its fundamental characteristic is that it largely relies on external resources. Establishing it requires time and expense, and once established, it is difficult to change. Therefore, it is a strategy that must be formulated with a medium- to long-term perspective.
5 Backend Systems
We are now in the era of DX (Digital Transformation), where IT systems have become indispensable for various business operations. It is essential to design, build, and integrate systems behind the scenes—invisible to users and employees—to streamline operations.
6 KPI/KGI Design
KPIs and KGIs refer to specific numerical targets serving as metrics. Even when quantification isn’t possible, measuring the effectiveness of strategy execution through surveys or internal/external interviews is crucial for enhancing and refining initiatives. Furthermore, the methods for improvement based on these effects are not fixed; it is important to adapt them according to the situation.
■Strategic Attribution
By sharing the setting of the KPI required by the company, analyzing the measurement of the effect by the promotion implementation, circling the PDCA, we will achieve the achievement of the problem.
5Management
Management refers primarily to the methods used to manage various resources, assets, risks, and other elements within a business context, aiming to optimize operational effectiveness. While management is generally translated as “control,” the various management theories developed from management science encompass not only the meaning of ‘control’ but also elements such as “evaluation, analysis, selection, improvement, avoidance, integration, planning, coordination, direction, control, and organization.” The comprehensive concept encompassing these elements is called management activities.
1 Leadership
Leadership refers to the ability to steer an organization. It is required to achieve organizational goals, regardless of the scale of the department, division, or project. Communicating organizational goals and explaining how these goals link to management policies are also essential leadership competencies.
2 Organizational Structure Design
There is no single, universally optimal organizational structure for all situations. Designing the most suitable structure for each context is critically important for business operations. When considering organizational structure, it must be designed in a balanced manner, taking into account corporate goals (vision, mission, objectives), management strategy, business strategy, functional strategy, technology (IT and others), the business environment, and human resources factors, thereby enhancing the company’s competitiveness.
3 Human Resource Management
We assess whether the desired talent profile aligns with management philosophy and business plans, then formulate new HR and training strategies. HR strategy is essential for securing the optimal talent resources for the company. Beyond new hires, it is critical to determine how effectively we can elicit voluntary cooperation from existing talent resources to achieve corporate goals and strategic objectives. Training strategy is closely linked to HR strategy. To appropriately deploy human resources as a strategic asset and foster further growth, it is necessary to provide diverse learning opportunities tailored to objectives. This includes enhancing managerial coaching skills and establishing seminar and training programs.
4 Financial Management
Enhancing corporate value requires not only executing management and business strategies but also strengthening the financial foundation supporting the company. It is crucial to achieve an optimal capital structure by planning and executing various financial measures. Failure to operate financial functions appropriately can lead to a shortage of necessary funds resulting in bankruptcy, or to a situation where investment returns fall below interest rates, causing increasing cash outflows and destroying shareholder value. The mission of financial strategy is to avoid such situations and, more proactively, to maximize/optimize shareholder value through careful consideration of funding and investment.
5 Backend
Generally, “backend” refers to the parts of a website or web application not directly visible to users (such as server-side systems and databases). However, at 6e, we use the term more broadly to mean “the overall framework for executing initiatives and the associated system integrations.”
6Operations
Once a strategy is established, it is not easily changed. However, as the strategy is implemented, it is crucial to verify its effectiveness and results, and to make improvements where bottlenecks are identified. In operations, following the PDCA cycle (repeating the four stages: Plan → Do → Check → Act), post-implementation reviews are conducted on the results of executed strategies. Feedback from these reviews is used to refine the strategy, making it more precise.
1 Business Operations
Daily corporate activities themselves constitute operations. They form the critical foundation supporting corporate management and serve as a source of competitiveness. Optimal operations are the backbone of corporate management, and their thorough implementation throughout the company is vital for strategic execution.
2 Sales Strategy
Sales strategy comprises three components: “Sales Territory,” “Sales Plan,” and “Sales Activities.” It is vital to clearly define the target audience for products or services and determine the appropriate tools, media, and methods without misdirection. The key point of sales strategy is to meticulously tailor all elements to the specific circumstances at hand.
3 Verification and Improvement Meetings
Regular meetings are held to review the results of executed plans and to check for deficiencies or issues during ongoing execution. These meetings primarily serve as project reviews to determine whether actions succeeded, failed, or are still insufficiently advanced.
4 KPI・KGI
KGI (Key Goal Indicator) represents the ultimate goal a company must achieve within a specific period. KPI (Key Performance Indicator) refers to the intermediate goals set incrementally to achieve the KGI.
5 Meeting Methods
Meetings incur significant labor costs. Each participant must clearly understand the meeting’s purpose and prepare accordingly. When everyone attends meetings with cost awareness, meetings proceed smoothly, contributing to the company’s growth.
